-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non invasive, safe, medical imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues in our body.
-
MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT).
-
It is the world’s highest level of imaging modality in the medical field till date.
-
MRI is considered as gold standard for the evaluation of the Brain, spine and musculoskeletal system as it gives excellent anatomical detail which helps in the characterization of various diseases.
-
One of the important facts about MRI is that it is safe for the human body. It does not cause harmful effects of radiation on the body as it uses a magnetic field to produce detailed images.
-
MRI is safe during pregnancy.
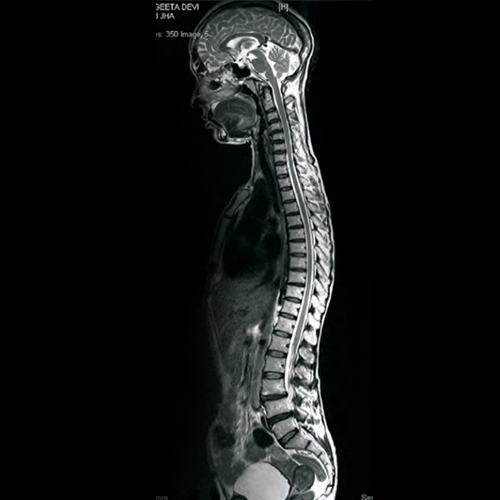
MRI spine is considered as gold standard for the evaluation of spinal diseases as it gives excellent details of Spinal cord, Nerve roots, Intervertebral discs, Bony vertebrae and Spinal ligaments.
Indications
-
Radiculopathies (Backache , neck pain etc)
-
Degenerative spine diseases
-
Cord tumor
-
Spinal infections (Tuberculous / Pyogenic etiology)
-
Postoperative evaluation (for infection)
-
Spinal cord Trauma
-
Congenital malformations of the spinal cord, cauda equina or meninges
-
Myelopathy
-
Demyelinating disease
-
Any cause of spinal disease in pregnancy
Causes of back pain are degenerative spine diseases, Infections like Tuberculous / pyogenic spondylitis, spinal cord tumor, Demyelinating disease, or any myelopathy.
Case 1:
Patient with back ache and leg pain, clinically suspected as degenerative Disc disease, MRI Spine revealed Spinal meningioma.
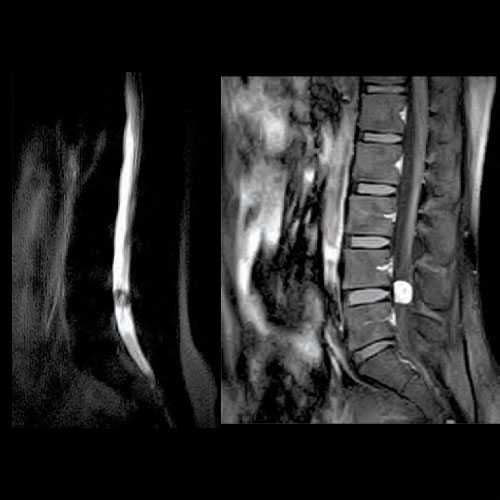
Case 2:
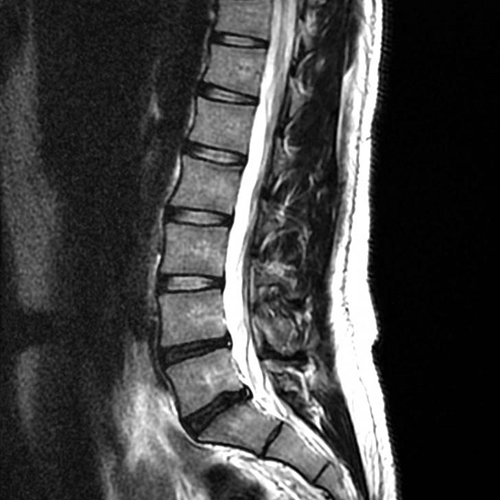
Old age patient with backache (without leg pain) since 3 months (X-ray LS spine was normal), MRI lumbar spine revealed lumbar Bony and neural metastasis. Retrogradely confirmed as case of Ca. Prostate.
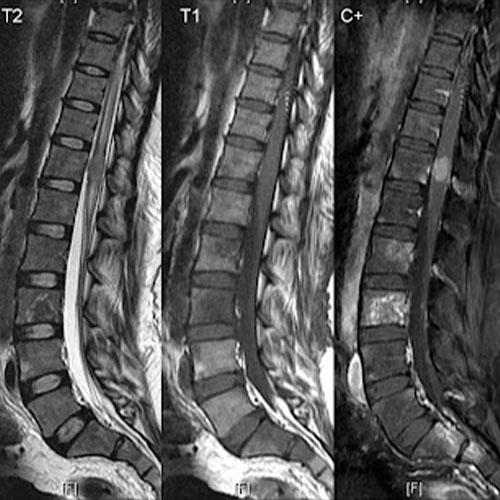
Patients with Backache with or without Radiculopathy can have lumbar disc herniation, Disc infection, Lumbosacral neuritis, nervesheath tumor, meningioma, lumbar bony metastasis, Early koch’s spine, pyogenic spondylitis etc. X-Ray LS spine will be normal in most of such patients.
MRI lumbar spine in such patients increases diagnostic confidence and satisfaction of both consultant and patient.
-
To identify the underlying pathology.
-
To differentiate surgical and nonsurgical candidates.
-
For knowing exact anatomical details of degenerative spinal pathology PRE-OPERATIVELY.
-
For exact localization of vertebral level before giving epidural block (Patients who refuse spinal surgery or in nonsurgical candidates).
-
To give the most appropriate therapy.
-
LAST BUT NOT LEAST, To know the overall prognosis of patients with back pain and radiculopathies(which will aid in patient satisfaction).
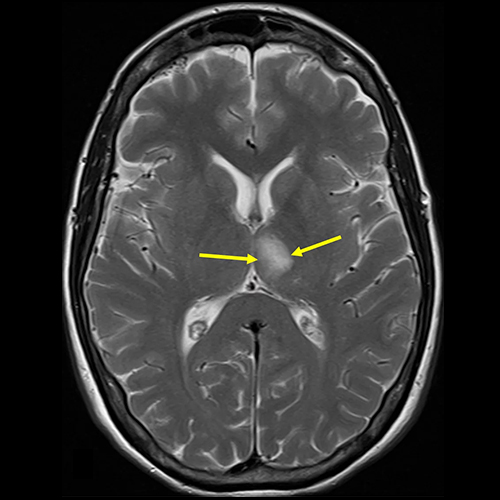
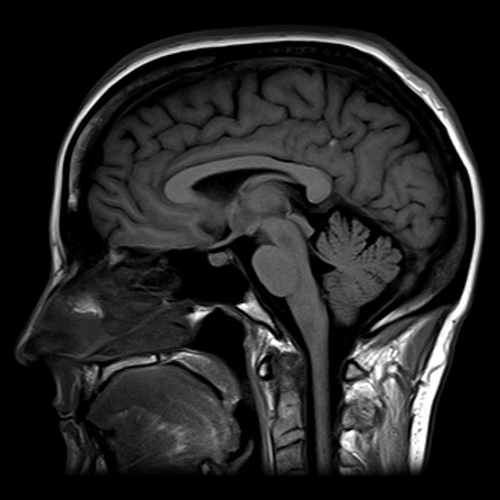
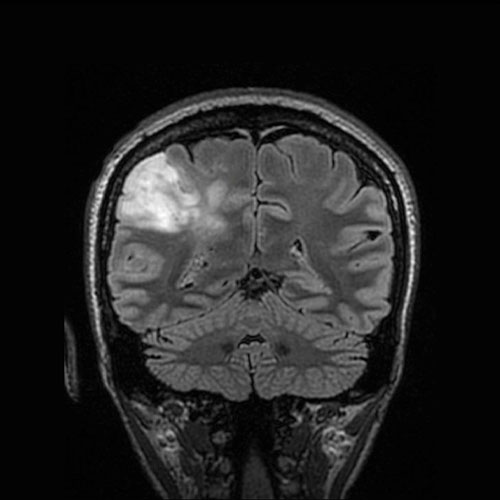
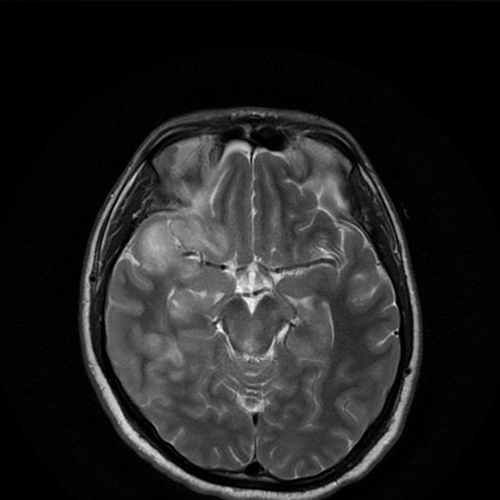
In patients with stroke:
MRI is increasingly being used in the diagnosis and management of stroke. It is much more sensitive and specific than CT-SCAN. It detects Ischemia as early as within half hour of symptoms onset while CT – SCAN takes 06 to 12 hrs for detection of ischemia after symptoms onset. MRI is the investigation of choice for evaluation of brain stem and cerebellar pathology, as pathology of these areas is often missed in CT-SCAN.
In adult patients with epilepsy / suspected Brain Tumour.
MRI is investigation of choice in adult patients with epilepsy or suspected brain tumour as it accurately detects size of the tumor and tumoral oedema which is a very important pre-operative consideration.
In patients with Trigeminal Neuralgia (5th Nerve Protocol).
With use of various MRI sequences and MRI angiography vascular compression of the trigeminal nerve can be demonstrated.
In patients with Head Injury : In patients with diffuse axonal injury CT – SCAN may be normal and MRI is an investigation of choice.
Other indications
-
Organic headache
-
Venous sinus thrombosis
-
Meningitis
-
Encephalitis
-
Metastatic disease
-
Infection
-
Multiple sclerosis
-
Post-surgical evaluation
-
Demyelinating disease of the brain
-
Congenital malformation of the brain or meninges
-
Encephalopathy
In Pediatric epilepsy :
For evaluating child with seizure , roll of MRI is
-
To identify underlying pathology.
-
To know prognosis.
-
To give most appropriate therapy.
Advantages of MRI in pediatric patients over CT – SCAN
-
Excellent soft tissue contrast (Nearly pick ups 100 % pathology).
-
No artifact in Basal Brain like CT – SCAN.
-
No hazards of ionizing radiation in pediatric patients (Roughly 1 CT BRAIN in pediatric patient give radiation equivalent to 100 chest X – ray)
-
“Ideally MRI should be performed in all pediatric patients with seizures except idiopathic generalized epilepsy and Benign Rolandic Epilepsy of childhood.”
Because
A high level of soft tissue resolution in MRI gives better grey white matter differentiation which helps to detect even the smallest pathology.
Radiation: MRI has no harmful radiation. This will be particularly helpful in pediatric patients and patients of reproductive age group.
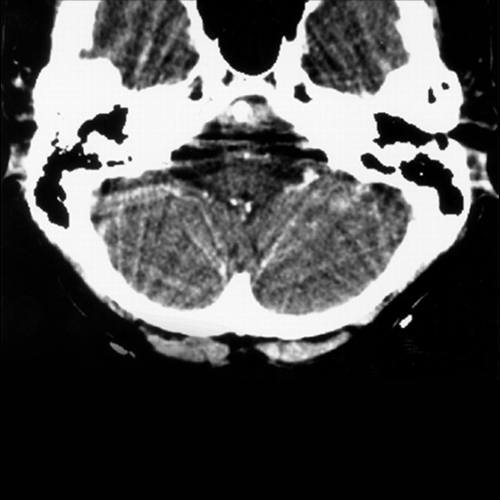
Skull base artifacts in CT-Scan
Due to crisscross artifacts in CT Scan at the skull base, the following areas are not properly evaluated in CT Scan images:
Cerebellum, Midbrain, Pons, Medulla, Basal temporal region, Basal frontal region, Pituitary gland, Cavernous sinus, etc.
Pathology in the above-mentioned areas is frequently missed in CT scan images.
MRI brain is preferred over a CT scan in all clinical situations NOWADAYS. i.e. Headache, giddiness, stroke, epilepsy, psychiatric illness, ophthalmic indications, etc.
Currently, Acute trauma to the brain is the only absolute indication for CT-Scan brain.
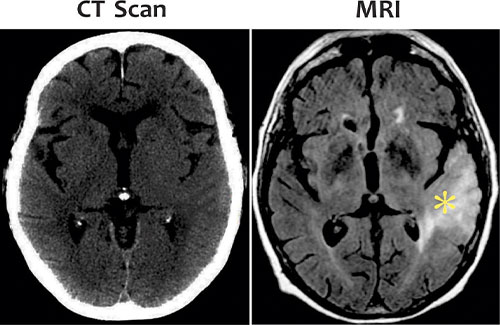
CT Scan
MRI
In patients with non-traumatic hemorrhage, MRI is superior to a CT scan to find out the underlying cause of hemorrhage like Hemorrhagic metastasis/tumor, Cortical vein /venous sinus thrombosis, Vascular malformations etc.
A normal or positive MRI. both increases diagnostic confidence and satisfaction of both consultant and patient
Comparative images of CT Scan & MRI of the patient with intermittent headache and recent epilepsy reveals low grade tumor in temporal lobe in MRI. Previous CT SCAN of the same patient before few days reveals almost no abnormality.
⇒
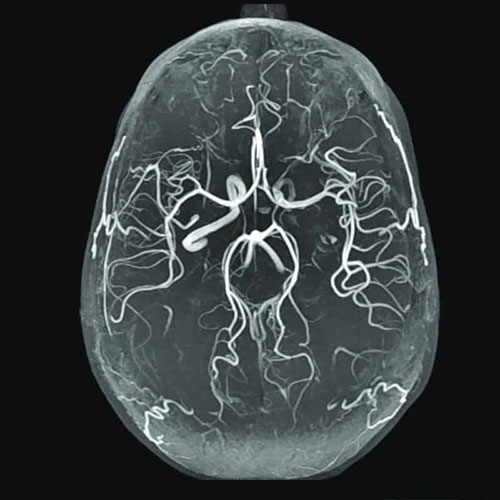
A specialized MRI ordered to evaluate arteries
Indications
-
Aneurysm
-
Stenosis/occlusion related to stroke, or carotid stenosis
-
Dissection (a tear in the artery wall that can cause stroke)
-
AVM’s (arteriovenous malformations).
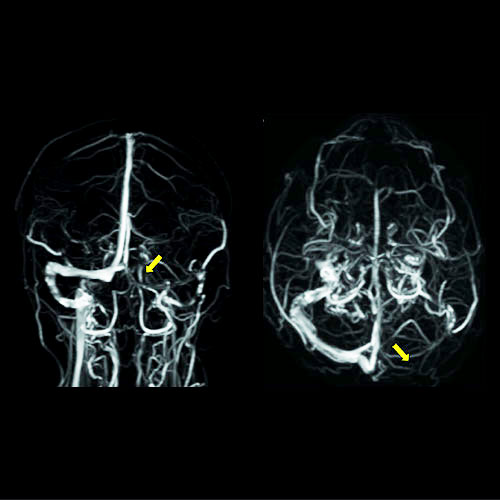
A specialized MRI brain is ordered to evaluate the veins of the head.
Indications:
-
In patients with venous infarcts (Venous sinus thrombosis / Cortical vein thrombosis) MR venography is an investigation of choice.
-
Venous drainage of AVM’s
MR Venography and Angiography are non invasive techniques which does not involve injection of contrast media.
-
Tumours / Infections arising in bone or other connective tissue.
-
Knee: Ligaments/meniscus injuries.
-
Shoulder: rotator cuff injury.
-
Osteonecrosis
-
Derangement of the hip, knee, ankle, shoulder, elbow or wrist joints or their supporting structures
-
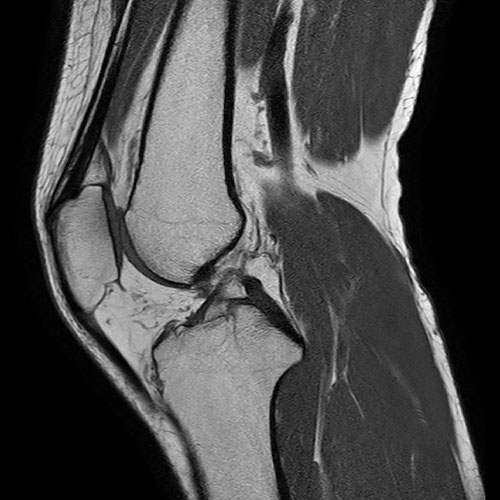
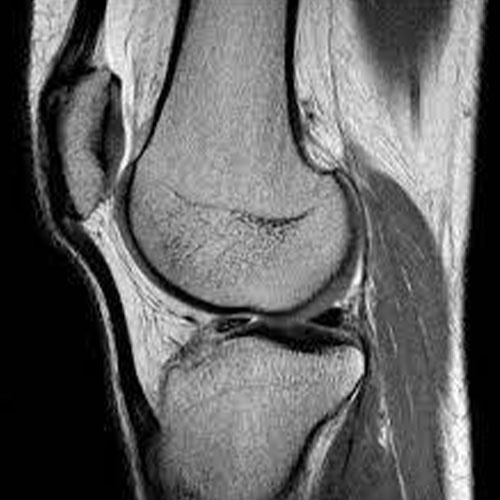
MRI is the gold standard in the evaluation of soft tissue injuries of the knee.
-
Undetected / Untreated knee injuries of ligaments will lead to the development of premature osteoarthritis in young patients.
-
Ideally, every knee injury patient should be evaluated with an MRI
-
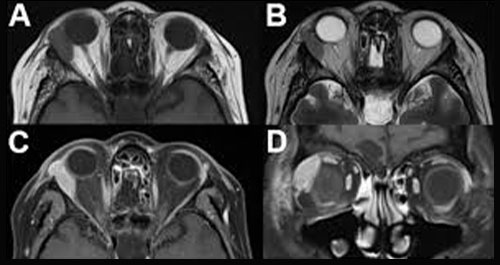
Orbital tumors
-
Optic neuritis.
-
Suspected intra-orbital or visual pathway lesions
-
Dysthyroid eye disease
-
Diplopia
-
Etc
-
-
Any electrically, magnetically, or mechanically activated implants (including cardiac pacemakers, biostimulators, neurostimulators, cochlear implants, and hearing aids).
-
Patients who have a metallic foreign body (metal sliver) in their eye
-
Intracranial aneurysm clips (Unless the referring physician is certain that it is made of nonferromagnetic material such as titanium).
-

